IGMP snooping is a feature that prevents unnecessary multicast traffic from being forwarded.
Normally, multicast traffic is flooded to all affiliated ports in the samenetwork, which wastes bandwidth by forwarding multicast traffic to ports where no multicast receiving terminal exists.
In contrast, if IGMPsnooping is enabled, it saves bandwidth by only forwarding the necessary multicast traffic to ports with a receiving terminal connected.
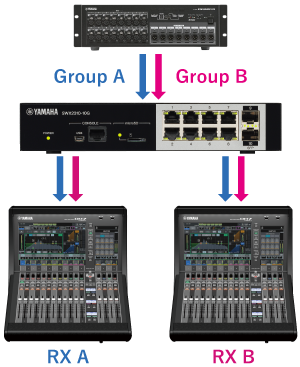
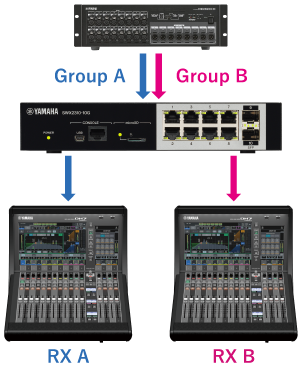
Thefollowing example shows the difference between flooding and IGMPsnooping, assuming receiving terminal A (RX A) only wants to receiveGroup A multicast traffic and receiving terminal B (RX B) only wants toreceive Group B multicast traffic.
Flooding forwards both Group A and Group B traffic to the port where RX A is connected, but IGMP snoopingonly forwards Group A traffic to the port where RX A is connected.
In the case of flooding |
In the case of IGMP snooping |
|
|
Switches with IGMP snooping enabled use "IGMP Query" and "IGMP Report" to learn which multicast group traffic should be sent to which ports.
The following example shows the process flow of processing IGMP queries and IGMP reports.
-
One representative switch in the network periodically sends IGMP queries. The switch that sends the IGMP queries is called the "Querier".
-
When the multicast receiving terminal receives an IGMP query, itsends an IGMP report in response. The IGMP report contains informationabout the multicast group traffic that the receiving terminal wants toreceive.
-
The switch learns which multicast group traffic to send to which port by snooping on the content in IGMP reports.
Since learned multicast group information is automatically deletedafter a certain period of time, in order to maintain the correctlearning state one querier must always be present in the same network.
If multiple queriers exist in the same network, only one querier isretained and the other switches automatically stop sending queries.
Note that even if there is no querier, the receiving terminal mayspontaneously send an IGMP report, such as when the multicast receivingapplication is started in the receiving terminal.
Note that ifmulticast group information is learned without a querier present, thecorresponding multicast group traffic might not be forwarded to portswhere other receiving terminals are connected.